Client Case Studies
Investigating Radiation-Induced Heart Disease Mechanisms and Effects of Partial Heart Irradiation
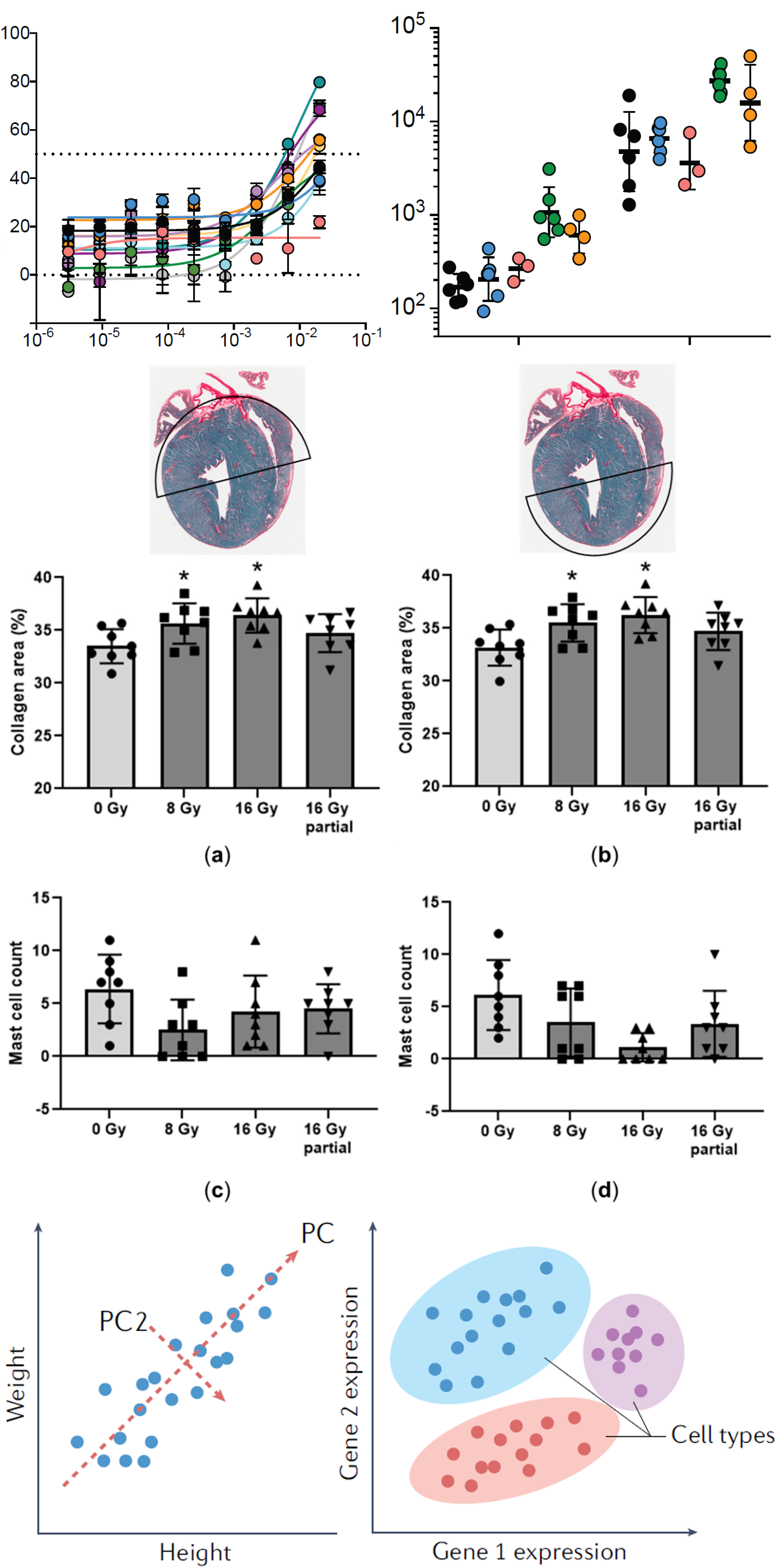
Context, Radiation therapy for chest tumors, such as lung or esophageal cancer, can inadvertently expose part of the heart to radiation, potentially leading to radiation-induced heart disease. The mechanisms behind radiation causing long-term injury to the heart remain unclear. A better understanding of these mechanisms and the effects of partial heart irradiation is crucial for improving patient outcomes and developing new intervention strategies.
Perspective: Nelson Scientific Labs, a leading research facility, stepped in to assist with a study designed to investigate the mechanisms of radiation-induced heart disease using mouse models. The lab's cutting-edge technology and expertise in pre-clinical research models provided an invaluable resource for the researchers, enabling them to collect and analyze critical data to further their understanding of the problem.
Analysis: Nelson Scientific Labs' technology allowed researchers to expose adult male and female mice to whole heart irradiation or partial heart irradiation (only 40% of the heart) to simulate the potential exposure that may occur in patients undergoing radiation therapy for chest tumors. Plasma samples were collected at 5 days and 2 weeks post-irradiation for metabolomics analysis. At 6 months post-irradiation, Nelson Scientific Labs helped examine cardiac collagen deposition, mast cell numbers, and left ventricular expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in both irradiated and unirradiated parts of the heart.
Result: With Nelson Scientific Labs' assistance in data acquisition and analysis, the researchers found small differences in the plasma metabolite profiles between the groups, but no significant differences in collagen deposition, mast cell numbers, or TLR4 expression between the irradiated and unirradiated portions of the heart. An increase in TLR4 expression was observed only after a single dose of 8 Gy to the whole heart. The results suggest that adverse tissue remodeling was not different between the irradiated and unirradiated portions of the mouse heart, and no clear differences were observed between male and female animals.
Benefit: The collaboration with Nelson Scientific Labs has provided essential insights into the mechanisms of radiation-induced heart disease and laid the foundation for future research. Additional work in larger animal cohorts will be necessary to confirm the lack of differences between male and female animals and to investigate the inhibition of TLR4 as a potential intervention strategy for radiation-induced heart disease.
References:
Sridharan, V.; Krager, K.J.; Pawar, S.A.; Bansal, S.; Li, Y.; Cheema, A.K.; Boerma, M. Effects of Whole and Partial Heart Irradiation on Collagen, Mast Cells, and Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Heart. Cancers 2023, 15, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020406
Nelson Scientific Labs provides comprehensive multi-omics services, from study design all the way to interpreting and reporting your findings.
Contact us today to find out how we may help you with your project!












